Blog Amal Fahmi – Organoids
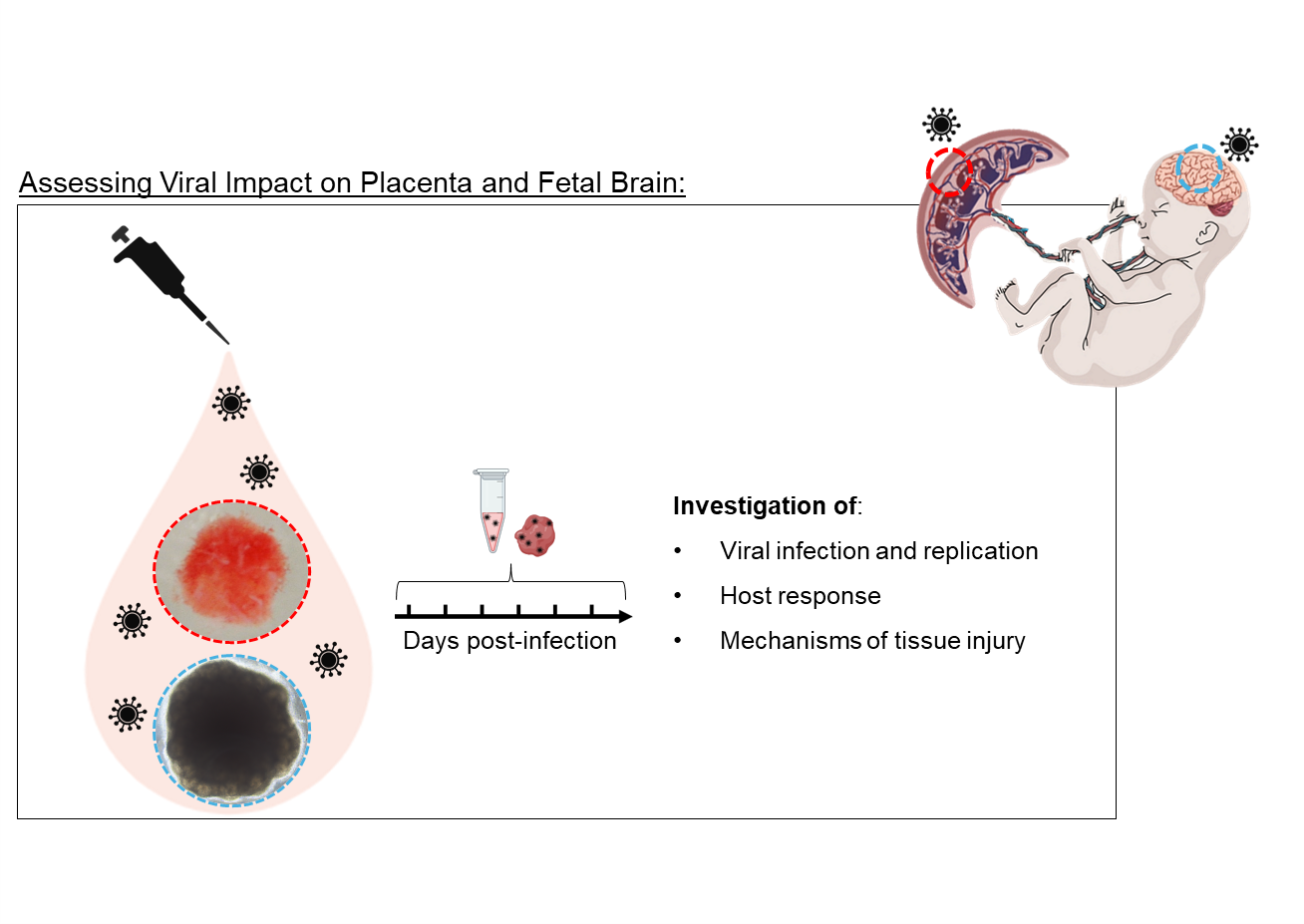
Studying the impact of viral infections on the placenta and foetal brain using ex vivo models and 3D organoids
Viral infections during pregnancy increase the risk of complications for both pregnant women and their foetuses. Examples include worse symptoms, higher miscarriage rates and potential developmental changes, especially in the brain. The placenta acts as a vital barrier during pregnancy but this protective function can sometimes be impaired when viral infections cause viraemia in pregnant women. In such cases the virus may cross the placental barrier, potentially jeopardising the well-being of the foetus and affecting its development, including that of its brain. To understand the underlying mechanisms, researchers need in vitro human models that faithfully reproduce viral infections in placental tissue and foetal brain tissue. To do this, we used sophisticated models such as human placenta explants and brain organoids to study infections caused by SARS-CoV-2, West Nile virus (WNV) and Zika virus (ZIKV). These models enabled us to study cellular tropism and viral propagation, and to characterise host responses to infection.